Boolean algebra#
Introduction#
Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra that deals with binary variables and operations, named after its founder George Boole. It plays a fundamental role in digital electronics, computer science, and mathematical logic. Boolean algebra is essential for designing and analyzing digital circuits, creating logical expressions, and simplifying complex logical statements.
Basics#
Boolean Variables#
Boolean algebra operates on binary variables that can have only two values: true (1) and false (0). These values are often represented as “T” and “F” or “1” and “0.”
Boolean Operators#
Boolean algebra uses three primary operators: AND, OR, and NOT. These operators manipulate Boolean variables to produce logical results.
AND (Conjunction): Denoted by ∧ or *, it returns true (1) only when both inputs are true (1).
A |
B |
A ∧ B |
|---|---|---|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
OR (Disjunction): Denoted by ∨ or +, it returns true (1) when at least one input is true (1).
A |
B |
A ∨ B |
|---|---|---|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
NOT (Negation): Denoted by ¬ or ', it returns the opposite of the input.
A |
¬A |
|---|---|
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
Boolean Expressions#
Boolean expressions are combinations of Boolean variables and operators. They can be used to represent logical conditions and are the building blocks of more complex logical statements.
Boolean Algebra Laws#
Boolean algebra follows several important laws and rules that help simplify and manipulate expressions.
Commutative Laws#
AND: A ∧ B = B ∧ A
OR: A ∨ B = B ∨ A
Associative Laws#
AND: (A ∧ B) ∧ C = A ∧ (B ∧ C)
OR: (A ∨ B) ∨ C = A ∨ (B ∨ C)
Distributive Laws#
AND over OR: A ∧ (B ∨ C) = (A ∧ B) ∨ (A ∧ C)
OR over AND: A ∨ (B ∧ C) = (A ∨ B) ∧ (A ∨ C)
Identity Laws#
AND: A ∧ 1 = A
OR: A ∨ 0 = A
Null Laws#
AND: A ∧ 0 = 0
OR: A ∨ 1 = 1
Domination Laws#
AND: A ∧ ¬A = 0
OR: A ∨ ¬A = 1
Double Negation Law#
¬(¬A) = A
Boolean logic gates#
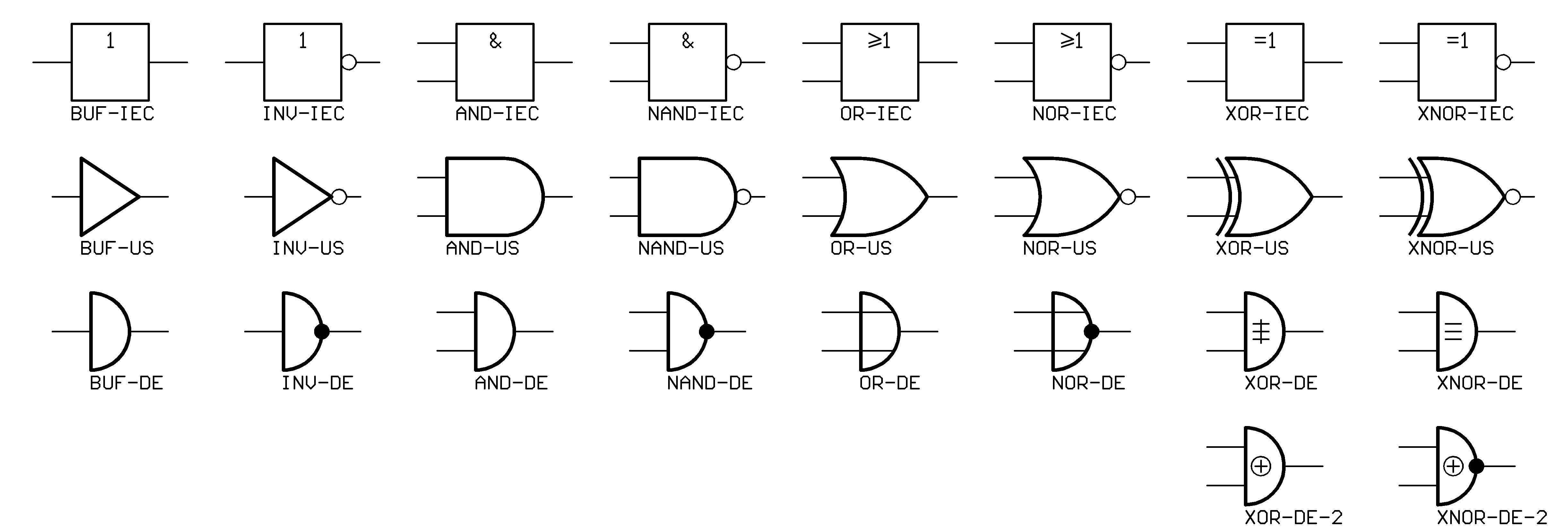
Boolean logic gates are fundamental building blocks of digital electronic circuits. These gates perform basic logical operations on one or more binary inputs (0 or 1) and produce a binary output based on specific logical rules. These gates are essential for constructing complex digital circuits and implementing logical functions in various electronic devices and computer systems. There are several types of common Boolean logic gates:
AND Gate:
Symbol:
A ----┌─── B ----│ AND └───Function: Outputs 1 (true) only when both inputs A and B are 1.
A
B
Output
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
OR Gate:
Symbol:
A ----┌── B ----│ OR └──Function: Outputs 1 (true) when at least one of the inputs A or B is 1.
A
B
Output
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
NOT Gate:
Symbol:
A ----┌─── │ NOT Q ----└───Function: Outputs the opposite value of the input A.
A
Q
0
1
1
0
NAND Gate:
Symbol:
A ----┌─── B ----│ NAND └───Function: Outputs 0 only when both inputs A and B are 1; otherwise, it outputs 1.
A
B
Output
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
NOR Gate:
Symbol:
A ----┌── B ----│ NOR └──Function: Outputs 1 only when both inputs A and B are 0; otherwise, it outputs 0.
A
B
Output
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
XOR Gate (Exclusive OR):
Symbol:
A ----┌─── B ----│ XOR └───Function: Outputs 1 when the number of 1s in the inputs A and B is odd.
A
B
Output
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
These logic gates can be combined to perform more complex logical operations and are the building blocks for designing digital circuits, such as adders, multiplexers, flip-flops, and processors. Digital computers and many electronic devices rely on combinations of these gates to process and manipulate binary data.
Boolean Algebra Applications#
Boolean algebra finds extensive applications in various fields:
Digital Logic Design: Boolean algebra is the foundation for designing digital circuits, including logic gates, flip-flops, and memory units. It allows engineers to create efficient and reliable electronic systems.
Computer Science: In computer science, Boolean algebra is used to design algorithms, control flow, and decision-making processes in programming. It plays a crucial role in conditional statements and loops.
Information Retrieval: Boolean algebra is used in search engines and databases for information retrieval. Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) are employed to refine search queries and filter results.
Network Design: In networking, Boolean algebra helps design routing algorithms, address resolution protocols, and access control lists, enabling efficient data transmission and security.
Artificial Intelligence: In AI and machine learning, Boolean algebra is used to create decision trees, logical rules, and classifiers for various applications, including natural language processing and image recognition.